What is Rosacea: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Key Takeaways
- Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition marked by facial redness, visible blood vessels, bumps, and in some cases, eye irritation or skin thickening.
- Common triggers include sun exposure, spicy foods, stress, alcohol, extreme temperatures, and irritating skincare products.
- Medical treatments range from topical and oral medications to laser therapy and, in severe cases, surgery.
- A holistic approach—including gentle skincare, anti-inflammatory nutrition, stress reduction, and trigger avoidance—can significantly improve symptom control.
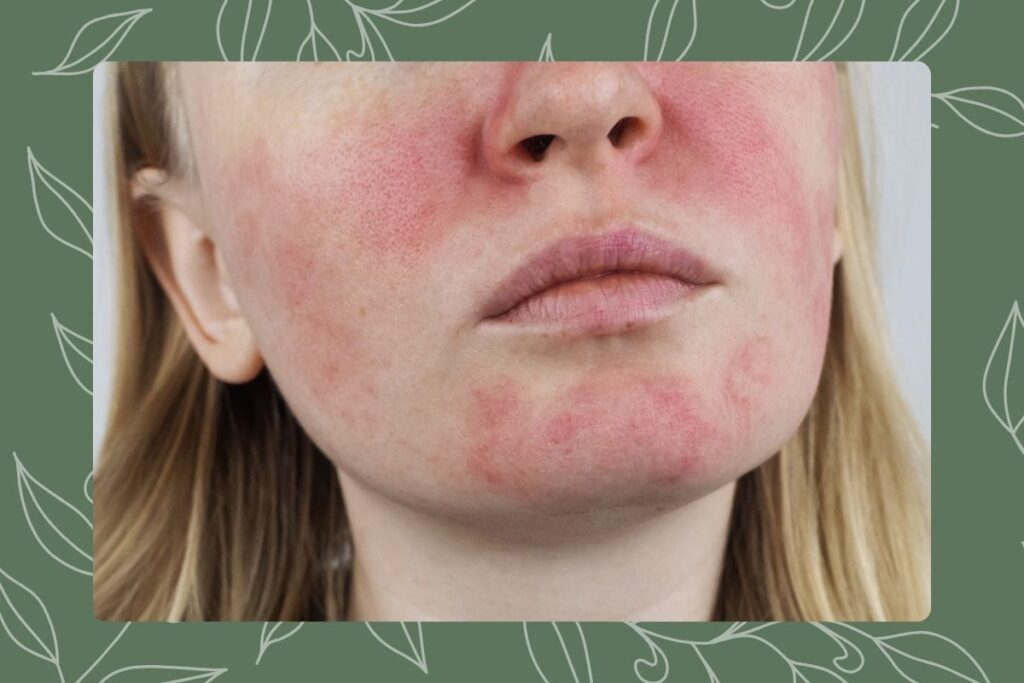
Rosacea is a chronic, inflammatory skin condition that predominantly affects the face, leading to redness, pimples, swelling, and visible blood vessels. Often mistaken for acne, an allergic reaction, or other skin problems, rosacea is a distinct disorder that requires targeted treatment and management strategies. This blog post delves into the details of what rosacea is, its types, causes, symptoms, and the various treatment options available. By understanding rosacea comprehensively, individuals can seek appropriate care and improve their skin health significantly.
What is Rosacea?
Rosacea is a chronic condition characterized by episodes of flushing and persistent facial erythema (redness). The condition typically progresses from episodic flushing triggered by various environmental or emotional stimuli to persistent redness, pimples, and vascular changes. It can also lead to rhinophyma (excess skin tissue around the nose) and ocular complications if left untreated. Rosacea is most common among adults between 30 and 60 years old, affecting both genders but tends to be more severe in men.
Types of Rosacea
Rosacea can present in various forms, and understanding these can guide better management:
- Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea (ETR): This subtype manifests as flushing and persistent central facial redness. Patients may also experience burning sensations and heightened skin sensitivity.
- Papulopustular Rosacea: Characterized by redness, swelling, and acne-like breakouts that come and go. This type can be easily confused with acne, but the skin is typically dryer and more sensitive.
- Phymatous Rosacea: This less common subtype involves thickening of the skin, irregular surface nodularities, and enlargement, typically of the nose (rhinophyma). It can be disfiguring and progressively worsen without treatment.
- Ocular Rosacea: Up to half of people with rosacea also experience eye symptoms, such as dry eye, irritation, and reddened, swollen eyelids. In severe cases, vision can be threatened.
What Causes Rosacea?
The exact cause of rosacea is still not fully understood, but several theories suggest it could be a combination of hereditary and environmental elements. Potential causes and contributing factors include:
Genetic predisposition
Rosacea tends to run in families, indicating a strong genetic component to its development. Individuals with a close family member who has rosacea are at a higher risk of developing the condition themselves. Research has identified several genes associated with rosacea, which may affect the immune system’s response or the integrity of the skin barrier. This genetic link explains why rosacea is more prevalent in certain ethnic groups, particularly those of Northern European descent.
Vascular irregularities
Abnormalities in facial blood vessels are a hallmark of rosacea, leading to easy flushing and persistent redness. These vascular irregularities may include an increased number of blood vessels and their dilation near the skin surface, causing the characteristic red appearance. Some theories suggest that these vascular changes could be due to regulatory problems in the body’s vascular control, or they might stem from environmental damage, particularly UV exposure.
Microorganisms
The skin mite Demodex folliculorum is notably more abundant in individuals with rosacea than in those without the condition. These microscopic mites reside in hair follicles and are believed to contribute to rosacea by blocking oil glands and causing inflammation. While not every person with rosacea has high levels of Demodex, their increased presence in affected individuals suggests a potential role in the development or exacerbation of the condition. The exact mechanisms through which Demodex mites influence rosacea remain under investigation, but their association with inflammation is a key area of focus for researchers.
Immune system factors
Recent advancements in research have pointed towards an overactive immune system as a potential underlying cause of rosacea. Certain immune system molecules, such as cathelicidins, which are part of the body’s innate defense system, are found in higher levels in rosacea patients. These molecules can promote inflammation and vascular changes when they are overproduced or not properly regulated. Additionally, external triggers like UV light or spicy foods might activate this immune response, worsening the symptoms of rosacea.
What Triggers Rosacea?
Several factors may trigger or exacerbate rosacea by increasing blood flow to the surface of the skin, including:
- Environmental factors: Sun exposure, hot or cold weather, wind, and humidity.
- Lifestyle factors: Hot baths, strenuous exercise, and the consumption of hot beverages or spicy foods.
- Psychological factors: Stress, anxiety, and sudden changes in emotion.
- Cosmetic products: Alcohol-based skincare products and those containing other irritants can worsen symptoms.
Symptoms of Rosacea
Rosacea’s symptoms vary widely but typically include:
- Facial redness and flushing: Central parts of the face such as the nose and cheeks are predominantly affected.
- Swollen red bumps and pimples: These may resemble acne but are usually accompanied by burning or stinging sensations.
- Visible blood vessels: Small blood vessels become visible on the skin of many people with rosacea.
- Eye issues: Ocular rosacea can lead to red, irritated eyes and swollen eyelids, which can result in eye dryness and potentially affect vision.
Rosacea Treatment Types
Effective treatment of rosacea requires a multifaceted approach:
- Topical treatments: Metronidazole, azelaic acid, and ivermectin are common topical medications used to reduce inflammation and redness.
- Oral medications: Antibiotics such as doxycycline or tetracycline are often used for their anti-inflammatory properties, not just their antibacterial effects.
- Laser and light-based therapies: These can help reduce the visibility of blood vessels and persistent redness.
- Isotretinoin: Reserved for severe cases, this powerful drug helps to control and prevent rosacea flare-ups.
- Dermatologic surgery: For advanced rhinophyma, surgical removal of excess tissue may improve both function and appearance.
How to Manage Rosacea Holistically
A holistic approach to managing rosacea not only involves medications but also lifestyle adjustments to minimize triggers:
Dietary modifications
To manage rosacea symptoms effectively, it is important to identify and avoid food and drink that trigger flare-ups. Common dietary triggers include hot and spicy foods, alcoholic beverages, and caffeine. Keeping a food diary can be a helpful way to track and identify specific foods that exacerbate one’s condition. Additionally, incorporating anti-inflammatory foods such as omega-3-rich fish, nuts, and leafy greens may help to reduce overall inflammation and improve symptoms.
Skincare routine
A gentle skincare routine is critical for those with rosacea. Using non-abrasive, fragrance-free, and hypoallergenic skincare products can prevent aggravation of the skin. It is advisable to avoid products that contain alcohol, witch hazel, menthol, peppermint, and eucalyptus oil as these ingredients can irritate sensitive skin. Moisturizing daily and using a mild cleanser can help maintain the integrity of the skin barrier, which is vital for managing rosacea.
Stress management
Stress is a well-known trigger of rosacea flare-ups, making effective stress management a key component of holistic care. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, deep-breathing exercises, or regular physical activity can significantly reduce stress levels. Additionally, establishing a routine that includes sufficient sleep and relaxation can help minimize the occurrence of rosacea symptoms related to stress.
Environmental considerations
Environmental factors play a significant role in triggering rosacea symptoms. Individuals with rosacea should take precautions to protect their skin from extreme weather—both hot and cold—and from sun exposure. Wearing hats and using broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher are essential when spending time outdoors. During winter, protecting the face from harsh winds with a scarf can also help prevent flare-ups.
Conclusion
Rosacea is a complex skin condition, but understanding its types, triggers, symptoms, and treatment options allows for better management and reduction of flare-ups. By combining medical treatments with holistic management strategies, individuals living with rosacea can lead a normal, active life with minimal discomfort.
FAQs
What triggers rosacea flare-ups?
Common triggers include environmental factors such as sunlight, extreme temperatures, and wind, as well as lifestyle factors like stress, spicy foods, alcohol consumption, and certain skin care products.
Is rosacea curable?
Rosacea is not curable, but it is manageable through medical treatments and lifestyle adjustments. Treatments aim to control symptoms and improve skin appearance, involving topical medications, oral antibiotics, and possibly laser therapy. Regular consultations with a dermatologist are essential to effectively manage the condition over time.
Can rosacea lead to other health problems?
Rosacea mainly affects the skin and eyes and is not typically linked to serious health issues. However, ocular rosacea can lead to eye complications like conjunctivitis and, in severe cases, corneal damage which might impair vision. There are also studies suggesting a potential link between rosacea and increased risks of cardiovascular and gastrointestinal diseases, but further research is needed to confirm these associations.
