Understanding Eczema: Causes, Symptoms, & Treatments
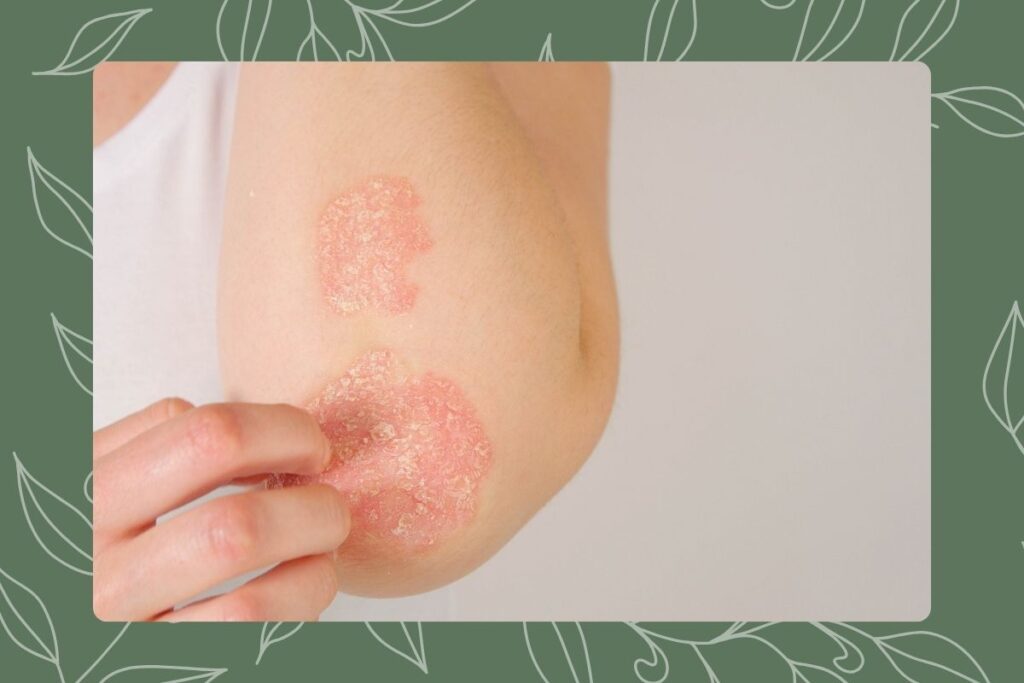
What is Eczema?
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition marked by itchy and inflamed patches. It’s typically a chronic issue, but it can improve, especially with proper treatment. Although it’s more prevalent in children, eczema can affect individuals of any age. The condition can vary in severity and can be influenced by genetic and environmental factors.
What is Dermatitis?
Dermatitis is a general term for skin inflammation. While eczema often refers specifically to atopic dermatitis, dermatitis can be caused by various factors and present in several forms. Dermatitis is characterized by red, itchy skin and can lead to blisters or scales.
Types of Eczema
- Atopic Dermatitis: The most common form, often hereditary and associated with other atopic disorders, such as asthma and hay fever.
- Contact Dermatitis: Triggered by contact with irritants or allergens, resulting in localized reactions.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: Characterized by small, itchy blisters on the hands and feet, often related to stress or moisture.
- Nummular Eczema: Presents as circular patches of irritated skin that can be crusted, scaly, and itchy.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Often appears on the scalp and face, presenting as scaly patches, red skin, and stubborn dandruff.
- Neurodermatitis: This condition is like atopic dermatitis but causes thick, rough patches on the skin, often from repeated itching and scratching in one area.
- Stasis Dermatitis: Mainly affects the lower legs when blood flow isn’t proper in the veins, leading to swollen, itchy, and sometimes painful skin.
What Causes Eczema?
The exact cause of eczema remains unknown, but it’s believed to be linked to genetic and environmental factors. The condition is often associated with a malfunction in the skin barrier, which allows moisture out and germs in, leading to dryness and vulnerability to irritants.
What Triggers Eczema?
Triggers can vary from person to person and can include:
- Environmental factors: Pollen, smoke, pollution, and changes in weather can exacerbate symptoms.
- Irritants: Soaps, detergents, fabrics, and fragrances can trigger flare-ups.
- Stress: Emotional stress is a known factor that can worsen eczema.
- Allergens: Dust mites, pets, pollens, and mold can trigger allergic reactions leading to eczema.
Symptoms of Eczema
- Dry, sensitive skin
- Intense itching
- Red, inflamed skin
- Dark colored patches
- Rough, leathery, or scaly patches
- Oozing or crusting
- Areas of swelling
Eczema Treatment Types
Treatment for eczema aims to heal the affected skin and prevent flare-ups of symptoms. Common treatments include:
Medications
Topical Corticosteroids
These are among the most common treatments for eczema flare-ups and work by reducing inflammation and itching. They come in various strengths and are usually applied directly to the affected areas. It’s important to use them as directed by a healthcare provider to avoid potential side effects, especially with long-term use.
Antihistamines
Over-the-counter or prescription antihistamines can help control itching, especially if it’s interfering with sleep. They work by blocking the action of histamine, a substance in the body that causes allergic symptoms like itching.
Moisturizers
Daily Moisturizing
A cornerstone of eczema care, moisturizing helps lock in the skin’s moisture, prevent dryness, and maintain the skin’s barrier. To maximize moisture retention, it’s recommended to use fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizers right after bathing.
Therapeutic Moisturizers
Some moisturizers are formulated specifically for eczema-prone skin and might contain ingredients that help repair the skin barrier, reduce water loss, and ease inflammation.
Therapies
Light Therapy (Phototherapy)
This involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of natural sunlight or artificial UV light under medical supervision. It can effectively reduce symptoms in some people, particularly those with severe eczema or when other treatments have failed.
Wet Wrap Therapy
This involves applying topical medications and moisturizers to the affected area and covering it with wet bandages. The wraps are then covered with dry bandages to hold in the moisture. This method can be particularly effective for intense flare-ups.
A Holistic Approach to Eczema Management
While topical treatments are fundamental in managing eczema, embracing a holistic approach can offer additional benefits and potentially address the root causes of eczema. This integrative strategy combines lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and stress management to complement conventional treatments, aiming for overall wellness and potentially reducing eczema flare-ups.
Diet and Nutrition
What you eat can influence your skin’s health. An anti-inflammatory diet may help reduce eczema symptoms. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon and flaxseeds, can be beneficial, as can a variety of fruits and vegetables, which are high in antioxidants and vitamins. Conversely, it’s wise to avoid foods that can trigger inflammation, such as processed foods, dairy, and refined sugars.
Stress Reduction
Stress is a well-known trigger for eczema flare-ups. Engaging in stress-reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help manage stress levels and may reduce the frequency and severity of eczema outbreaks.
Sleep and Exercise
Adequate sleep is crucial for skin repair and stress reduction, while regular exercise can improve circulation and help manage stress, potentially leading to fewer eczema flare-ups.
Natural Supplements
Certain supplements, such as probiotics, fish oil, and vitamin D, might improve eczema symptoms by supporting skin health and the immune system. However, consulting with a healthcare provider before starting any supplements is essential, especially if you are taking other medications.
Environmental Factors
Minimizing exposure to irritants and allergens in your environment can reduce eczema symptoms. Using a humidifier, choosing fragrance-free cleaning products, and wearing clothing made from natural fibers can all contribute to a skin-friendly environment.
Integrative Therapies
Some individuals find relief through alternative therapies like acupuncture or homeopathy. However, it’s important to approach these treatments under the guidance of qualified professionals and in conjunction with conventional medical advice.
Conquering Eczema
Eczema is a complex condition with various forms and triggers, but understanding and managing it can significantly improve your quality of life. Recognizing symptoms, identifying personal triggers, and implementing a targeted treatment plan can all help manage eczema effectively. With ongoing research and a growing range of treatment options, individuals with eczema have many resources at their disposal to control their symptoms and lead healthy, comfortable lives.
If you are struggling with eczema and looking for a holistic, tailored treatment plan, schedule a consultation today!
FAQs
1. What is eczema and why do people get it?
Eczema is a condition that makes your skin red, inflamed, and itchy. It’s often caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People with eczema may have a compromised skin barrier, which makes their skin more susceptible to irritants and allergens, leading to flare-ups.
2. Can eczema appear at any age?
Yes, eczema can develop at any age, although it is most commonly diagnosed in childhood. Some people may outgrow the condition as they age, while others may develop it for the first time as adults.
3. How is eczema diagnosed?
Eczema is typically diagnosed by a healthcare provider based on the history of your symptoms and a physical examination of your skin. In some cases, patch testing or other exams may be conducted to rule out other conditions or identify specific triggers.
4. Can eczema be cured?
There is no cure for eczema, but the condition can be managed through medical treatment and lifestyle adjustments. Treatments focus on healing the affected skin and preventing future flare-ups. This can include the use of moisturizers, prescription creams, and avoiding triggers.
5. Is eczema contagious?
No, eczema is not contagious. You cannot catch it from someone else or spread it to others. It’s typically a hereditary condition influenced by personal environmental exposures.
